
Top 10 Principles of Financial Management
Financial management is the backbone of any successful organization. It goes beyond simply handling money—it involves making strategic decisions that drive growth, ensure stability, and secure long-term sustainability. Understanding financial management principles is essential for businesses and individuals alike, as it allows them to maintain financial health, optimize resources, and navigate economic uncertainties effectively.
In this guide, we’ll explore the core principles of financial management, breaking them down into actionable insights that can help enhance your financial literacy and decision-making skills.
1. The Principle of Risk and Return
The foundation of any financial decision is the relationship between risk and return. Higher potential returns come with greater risk, while safer investments generally yield lower returns. Financial managers must carefully assess risk to maximize returns while safeguarding financial stability.
For example, investing in a startup offers high return potential but carries significant risk due to market volatility. On the other hand, government bonds provide stability with lower returns. Smart financial management involves using tools like risk assessment matrices and scenario analysis to balance risk and reward effectively.
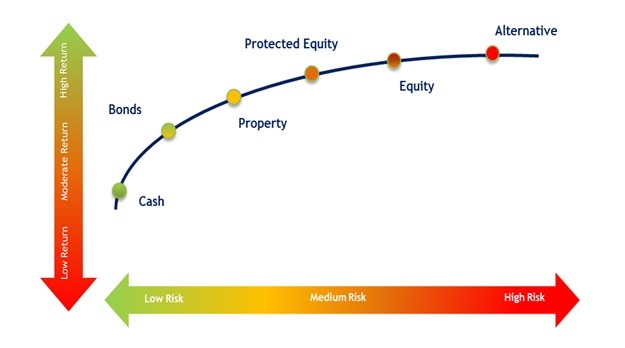
The Principle of Risk and Return
2. The Principle of Time Value of Money (TVM)
A dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future due to its earning potential. This principle is crucial in investment planning, as it determines how money grows over time.
For instance, choosing between receiving $10,000 today or $10,500 a year from now depends on factors like interest rates and inflation. Financial managers use formulas like present value (PV) and future value (FV) to assess investments and optimize cash flow management.

The Principle of Time Value of Money (TVM)
3. The Principle of Diversification
Diversification reduces financial risk by spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, or geographic regions. Relying too heavily on a single investment increases exposure to potential losses.
For example, a portfolio with only technology stocks might suffer during a tech industry downturn. A well-diversified portfolio that includes stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities provides better risk protection. Financial managers use asset allocation and sector diversification to enhance stability and returns.

The Principle of Diversification
4. The Principle of Cash Flow
Cash flow management is critical for financial stability. Positive cash flow ensures a company can meet short-term obligations, while negative cash flow can signal financial distress.
Financial managers monitor cash inflows and outflows through cash flow statements, ensuring there’s enough liquidity to cover expenses and invest in growth. Techniques like forecasting, budgeting, and working capital management help maintain a healthy cash flow.

The Principle of Cash Flow
5. The Principle of Profitability and Liquidity
Profitability fuels business growth, but liquidity ensures survival. Striking the right balance is key—focusing solely on profits while ignoring liquidity can lead to financial instability.
Financial managers analyze profitability ratios (e.g., net profit margin, return on assets) alongside liquidity ratios (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio) to ensure that businesses remain both profitable and financially stable.

The Principle of Profitability and Liquidity
6. The Principle of Financial Leverage
Leverage involves using borrowed funds to enhance returns. While it can amplify profits, excessive leverage increases risk and can lead to financial instability if investments underperform.
Financial managers use leverage ratios (debt-to-equity, interest coverage) to determine an optimal debt level. Stress testing and scenario analysis help assess how market fluctuations impact a company’s ability to meet debt obligations.

The Principle of Financial Leverage
7. The Principle of Cost-Benefit Analysis
Every financial decision should be evaluated by comparing its costs and benefits. Businesses should only undertake projects where the benefits outweigh the costs.
For instance, before launching a new product, financial managers analyze costs like production, marketing, and labor versus projected revenues. Tools like net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and payback period help determine whether a project is financially viable.
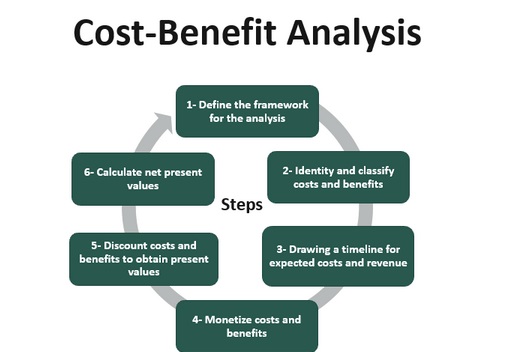
The Principle of Cost-Benefit Analysis
8. The Principle of Matching
Revenues and expenses should be recorded in the same period to accurately assess financial performance. This principle is crucial for transparent financial reporting and decision-making.
For example, if a business incurs costs in December but earns revenue from the related project in January, the expenses should be recognized in January. Financial managers use accrual accounting and adjust entries to ensure accurate financial reporting.
The Principle of Matching
9. The Principle of Prudence
Prudence encourages conservative financial decision-making. Overestimating revenues or underestimating costs can lead to financial difficulties. A cautious approach ensures realistic projections and financial stability.
Financial managers apply conservative estimates and recognize potential risks early, helping businesses prepare for uncertainties and avoid financial distress.
The Principle of Prudence
10. The Principle of Consistency
Consistency in financial practices ensures reliability and comparability over time. Stakeholders must be able to compare financial performance across different periods.
Financial managers maintain consistent accounting policies and financial reporting methods. Any changes in policies should be justified, disclosed, and applied retrospectively to ensure transparency.

The Principle of Consistency
Applying Financial Management Principles
To effectively apply financial management principles, a structured approach is essential. Here are the steps to implement them successfully:
- Set Clear Financial Goals – Define specific, measurable financial goals that align with the organization’s broader objectives. These goals provide a roadmap and a benchmark for assessing financial progress.
- Develop a Comprehensive Financial Plan – Create a detailed plan outlining the strategies and actions needed to achieve your goals. Include budgeting, forecasting, and resource allocation in this plan.
- Monitor Financial Performance – Regularly track financial performance against the plan. Use tools like financial ratios, cash flow analysis, and variance tracking to evaluate results and pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Make Informed Financial Decisions – Rely on financial analysis and cost-benefit evaluations to make smart decisions. Weigh the risks and rewards of each option to select the one best aligned with your goals.
- Establish Financial Controls – Put controls in place to ensure resources are used efficiently and financial policies are followed. Conduct periodic audits to detect and correct any deviations.
- Review and Adapt – Continuously review the financial plan and adjust it based on changing business conditions or performance outcomes. Stay flexible and ready to tweak strategies as needed.
What Is Financial Management and Why Is It Important?
Financial management is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and overseeing an organization’s financial resources to achieve its goals efficiently. It involves making strategic decisions about raising, allocating, and using funds to maintain financial health and ensure long-term success. Key tasks include budgeting, financial forecasting, risk management, and investment evaluation.
Here’s why financial management matters to businesses and organizations:
- Efficient Resource Allocation: It ensures limited resources, like capital, are distributed wisely across projects and operations.
- Boosting Profitability: It identifies profitable opportunities and cuts unnecessary costs to maximize earnings.
- Maintaining Cash Flow: A steady cash flow is vital for keeping daily operations running smoothly.
- Reducing Risks: It helps spot and manage financial risks, such as market fluctuations, credit issues, or liquidity challenges.
- Supporting Long-Term Planning: Financial management shapes financial goals, budgets, and strategies for sustainable growth.
- Smart Investment Choices: It guides the selection of promising investment projects through capital analysis.
- Enhancing Stability: A well-run financial system strengthens an organization’s resilience against uncertainties.
- Ensuring Compliance: It keeps organizations in line with financial regulations and reporting standards.
- Building Investor Trust: For public companies, strong financial management attracts and retains investors.
- Promoting Sustainability: It manages resources responsibly to support long-term viability.
In short, whether it’s a business, nonprofit, or government entity, financial management is a cornerstone of success. It’s about handling money wisely to optimize gains while minimizing risks, laying the groundwork for lasting growth. But what truly makes a robust financial management strategy so critical?
Financial management goes beyond handling money—it’s about making smart decisions that drive growth, stability, and risk management. By applying key Principles of Financial Management, individuals and businesses can strengthen their financial foundation, maximize profitability, and secure long-term success.
Effective financial management isn’t just about profits; it’s about creating value, managing risks, and ensuring stability. By following these Principles of Financial Management, anyone can navigate financial complexities and achieve their goals. Explore our Finance eBooks for expert insights and practical strategies.

Comments (0)