B2C E-Commerce: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Types, Benefits, Challenges, and Success Stories
In recent years, e-commerce has dramatically transformed the way businesses and consumers interact, reshaping traditional shopping experiences. Among the various e-commerce models, Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce has emerged as one of the most prominent and dynamic, revolutionizing retail across industries.
This article delves deep into the definition of B2C e-commerce, how it works, its different types, advantages, challenges, and examples of successful businesses that have thrived in this space.
What is B2C E-Commerce and How Does It Work?
B2C e-commerce refers to online transactions where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. Unlike Business-to-Business (B2B) e-commerce, where companies sell to other businesses, B2C focuses on end-users who make personal purchases.
The core objective of B2C e-commerce is to provide a convenient, seamless, and efficient shopping experience, enabling consumers to browse, select, and purchase products from anywhere with an internet connection.
How Does B2C E-Commerce Work?
The operational mechanism of B2C e-commerce follows a structured process:
- Setting Up an Online Store: Businesses establish an online presence through a website, e-commerce platform, or mobile app where they showcase their products/services with descriptions, images, and pricing.
- Consumer Browsing and Selection: Shoppers visit the website, explore product categories, read reviews, and compare options before making a selection.
- Shopping Cart and Checkout: Consumers add items to their virtual shopping carts and proceed to checkout.
- Payment Processing: Various payment methods, such as credit cards, digital wallets, or cryptocurrencies, are used to complete transactions.
- Order Fulfillment and Delivery: Businesses process and ship the purchased products, either directly from their warehouse or via third-party logistics providers.
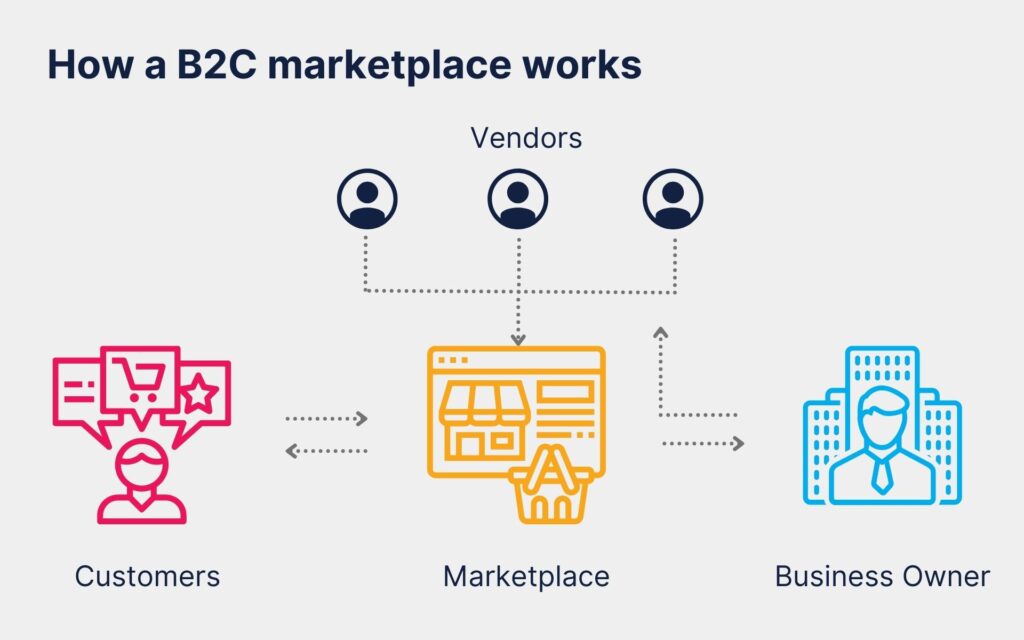
The operational mechanism of B2C e-commerce follows a structured process
B2C E-Commerce Growth and Market Value
The global B2C e-commerce market has been expanding at an unprecedented pace. In 2023, it was valued at approximately USD 5.8 trillion, and projections indicate a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.5% from 2024 to 2030. The increasing adoption of digital payment systems, mobile commerce, and AI-driven shopping experiences contribute to this growth.
Types of B2C E-Commerce: Key Models
B2C e-commerce can take different forms, each catering to specific consumer needs and preferences. Below are the most common types:
1. Direct Selling (Brand-Owned Stores)
- Businesses sell their products directly through their websites or proprietary e-commerce platforms.
- Examples: Nike, Apple, Samsung.
2. Online Marketplaces (Intermediary Platforms)
- Third-party platforms facilitate transactions between buyers and multiple sellers.
- These platforms handle payment processing, logistics, and customer service.
- Examples: Amazon, Alibaba, eBay, Shopee.
3. Community-Based Platforms
- These platforms focus on user-driven transactions, such as peer-to-peer (P2P) sales, social commerce, and online communities.
- Examples: Etsy (handmade goods), Airbnb (hospitality services), Poshmark (fashion resale).
4. Advertising-Based E-Commerce
- Businesses provide free content or services and generate revenue through advertising rather than direct sales.
- Examples: Google Shopping Ads, Facebook Marketplace, Instagram Shops.
5. Subscription-Based Services (Fee-Based E-Commerce)
- Consumers pay a recurring fee to access exclusive content, premium services, or curated product deliveries.
- Examples: Netflix (streaming), Spotify (music), Amazon Prime (premium shopping benefits).
Each model serves different consumer needs, allowing businesses to leverage digital tools, AI-driven recommendations, and personalized marketing to enhance customer engagement.
B2C e-commerce can take different forms
Advantages and Challenges of B2C E-Commerce
While B2C e-commerce presents remarkable opportunities, it also comes with challenges. Understanding both aspects is crucial for businesses looking to thrive in this competitive space.
Advantages of B2C E-Commerce
Global Reach & Market Expansion
Businesses can sell products worldwide without the limitations of physical stores.
Cross-border e-commerce enables companies to tap into new demographics and markets.
Convenience & 24/7 Accessibility
Shoppers can browse and buy anytime from their computers or mobile devices.
No constraints of store hours or physical location.
Personalized Shopping Experiences
AI and data analytics enable customized recommendations based on consumer behavior.
Personalized discounts and loyalty programs enhance engagement.
Lower Operational Costs
Eliminates costs associated with physical stores, rent, staffing, and utilities.
Automation streamlines inventory management and order processing.
Scalability & Flexibility
Businesses can easily expand product lines, integrate new technologies, and adapt to market trends without significant infrastructure changes.

Advantages of B2C E-Commerce
Challenges of B2C E-Commerce
Intense Competition
The saturated e-commerce market requires strong brand differentiation, compelling marketing, and customer loyalty programs.
Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks
Online transactions involve sensitive personal and financial data, making cybersecurity crucial.
Data breaches and fraud incidents can damage trust and credibility.
Logistics & Delivery Complexities
Order fulfillment, last-mile delivery, and supply chain management can be challenging, especially for cross-border shipping.
Customer Service & Returns Management
Handling customer complaints, product returns, and refunds efficiently is critical for maintaining a positive reputation.
Technology Dependence
A reliable e-commerce platform, secure payment gateways, and seamless UX/UI are essential for uninterrupted operations.
Examples of Successful B2C E-Commerce Companies
Several companies have excelled in the B2C space, setting benchmarks for innovation and customer experience:
- Amazon – The world’s largest e-commerce retailer, offering an extensive range of products and services with AI-driven recommendations and ultra-fast delivery (Amazon Prime).
- Alibaba – A global B2C and B2B powerhouse, connecting millions of buyers and sellers through platforms like Tmall and Taobao.
- Netflix – A leading subscription-based entertainment service, transforming the streaming industry with personalized content recommendations.
- Spotify – A global music streaming service that leverages subscription-based models and AI-driven playlists.
- Walmart – A retail giant that successfully expanded into e-commerce, integrating online and offline shopping for a seamless customer experience.
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce: Key Differences
While both B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C models use e-commerce, they cater to different audiences and operate differently:
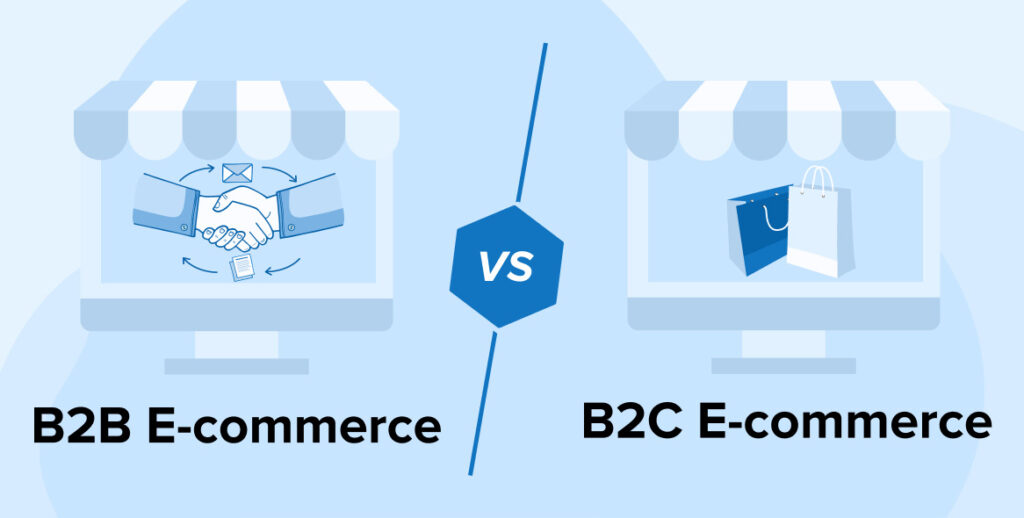
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce
| Feature | B2B E-Commerce | B2C E-Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Businesses & organizations | Individual consumers |
| Transaction Volume | Large bulk orders | Small individual purchases |
| Sales Cycle | Longer, negotiation-based | Shorter, direct purchases |
| Marketing Strategy | Relationship-driven, B2B content marketing | Influencer marketing, social media advertising |
| Payment Methods | Invoices, bank transfers, custom contracts | Credit cards, digital wallets, BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) |
B2C e-commerce continues to redefine the retail industry, offering businesses unprecedented growth opportunities and direct consumer engagement. However, success requires continuous innovation, strategic marketing, strong logistics, and robust cybersecurity measures.
By leveraging the power of digital technology, businesses can build customer-centric experiences, drive sales, and thrive in the evolving digital economy.

Comments (0)